
- #Mac unmount disk command line how to#
- #Mac unmount disk command line software#
- #Mac unmount disk command line mac#
- #Mac unmount disk command line windows#
Finally, type sudo diskutil unmountDisk force /dev/disk line.Then you need to find the disk that you want to force unmount.
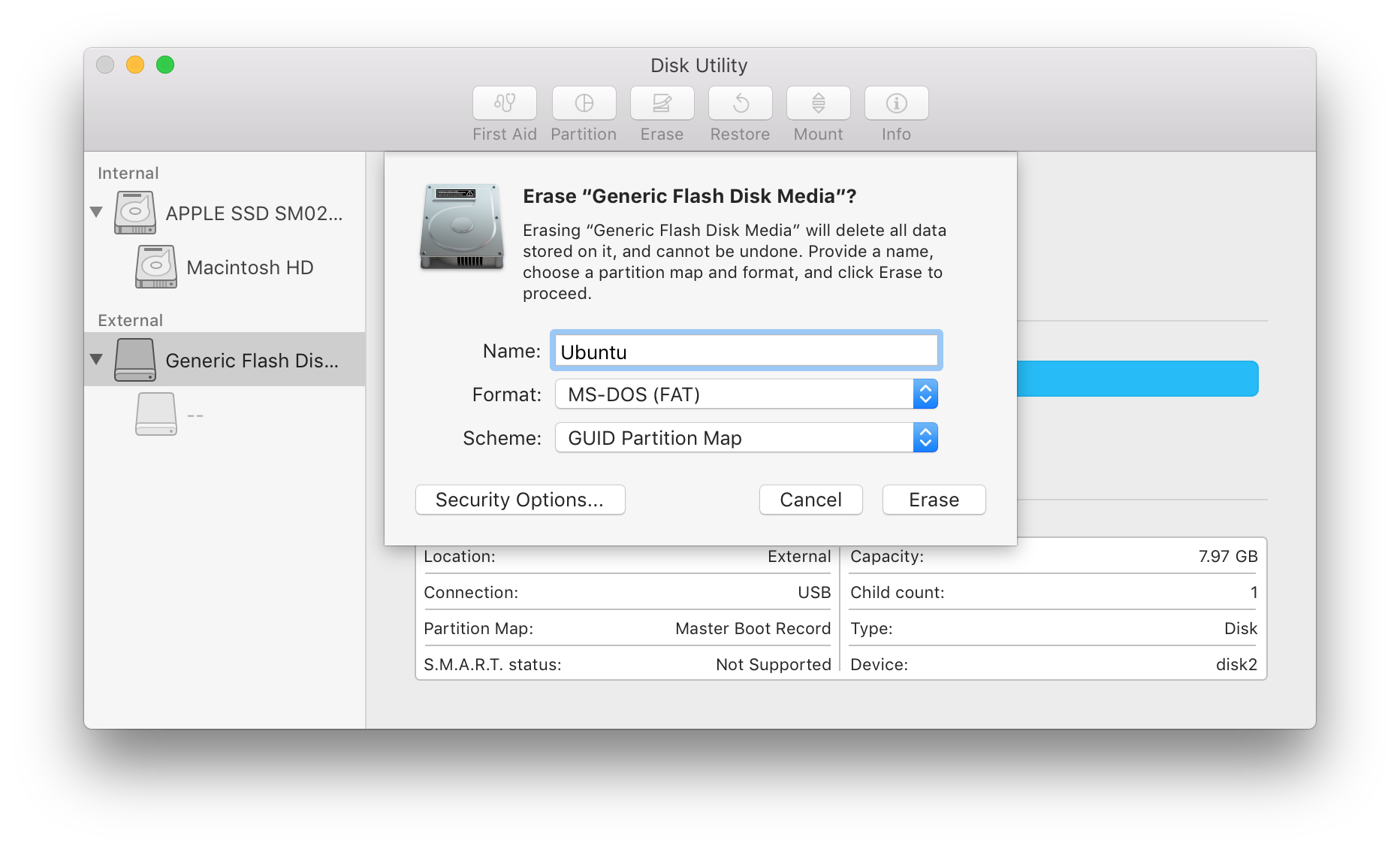
#Mac unmount disk command line software#
#Mac unmount disk command line how to#
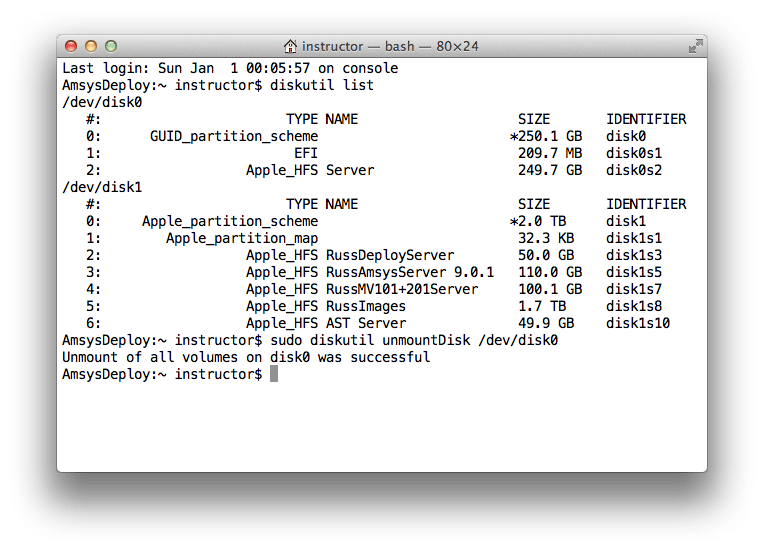
#Mac unmount disk command line mac#
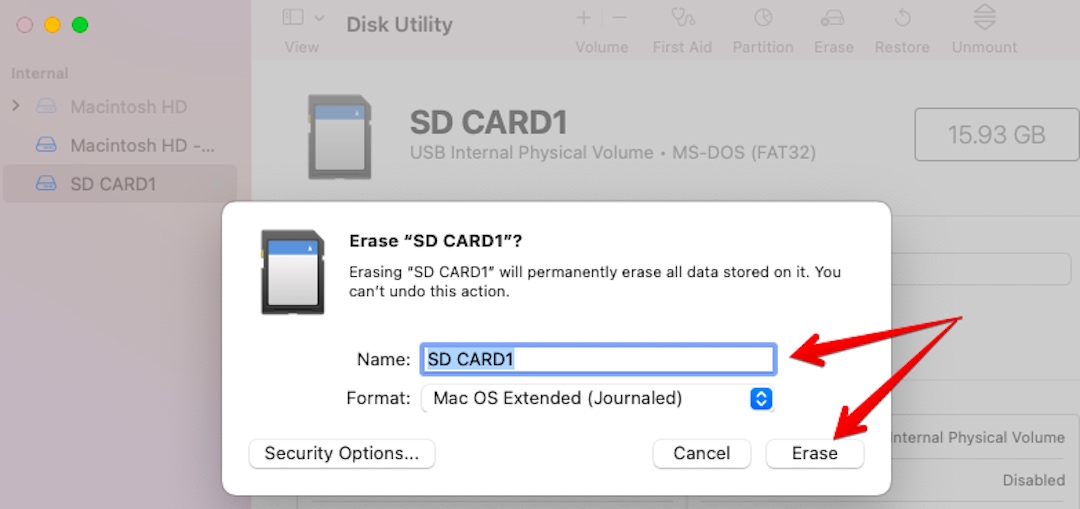
USB hard drives and flash drives would use similar syntax depending on what file system the device was formatted with eg. If the device was a HFS/HFS+ volume (Mac OS) then we would use this command: We check to see if our files and folders are there. Now it’s time to use all this information in the mount command For easy access let’s make a folder on the root called “drive2”. Now we create a folder to mount the drive to.
#Mac unmount disk command line windows#
In my example it is a Windows NTFS partition. Also CD’s and DVD’s take a while to show up sometimes so just repeat the command (use up arrow) until they do.Ĭheck the file system used by the drive we want to mount. Note this list seems to change and there is no guarantee that partitions named in the GUI using diskutil will have the same names here. dev/disk1s2 <- the file we want is here (we think) dev/disk0s1 <- we know we are on this partition We get some output which contains something like this: We use the ls command (similar to dir in DOS). We need to know what the computer has called our drives and partitions. You now need to be EXTREMELY CAREFUL about making inadvertent or damaging changes to root. The first command will check your disk for errors and the second will give you write access to the root. You can now go ahead and enter the two commands listed on the screen. This tells us that we are currently on disk 0, partition 1 (ignore the major, minor). For legit Mac users I think you hold Apple and s key as you boot.Īfter booting, somewhere on the screen, you should see a line similar to this: For Chameleon-type hackintosh bootloaders, hit any key then type –s enter. The folder we are going to mount the drive in.įirst we need to enter Single User Mode. The type of file system that drive uses.ģ. The name of the drive we want to mount (what do we call it?)Ģ. In order to use the mount command, we first need to know three pieces of information.ġ. Now if this was DOS, it would be trivial to copy the file over – not so in OS X. I knew I had to replace a certain file on the root with a file I had stored on another drive. Recently I had a situation where I couldn’t get into the GUI (even with safe mode –x).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
